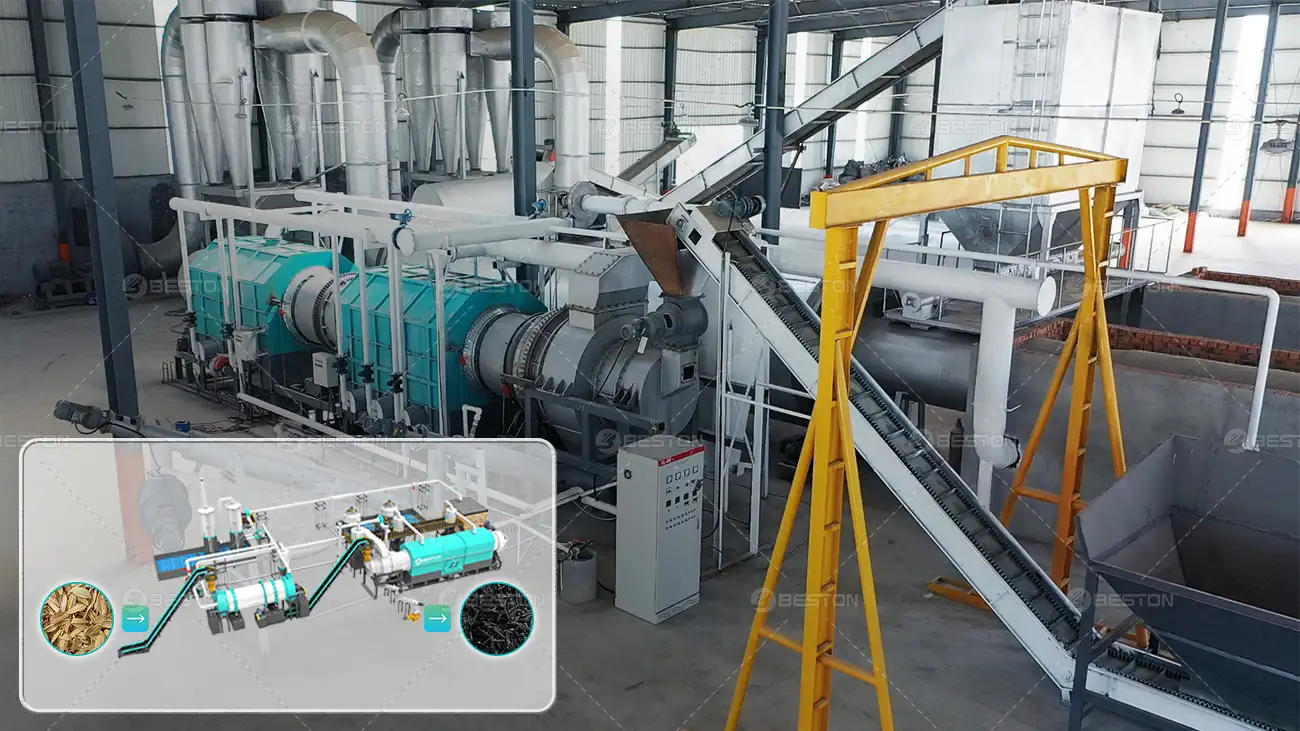
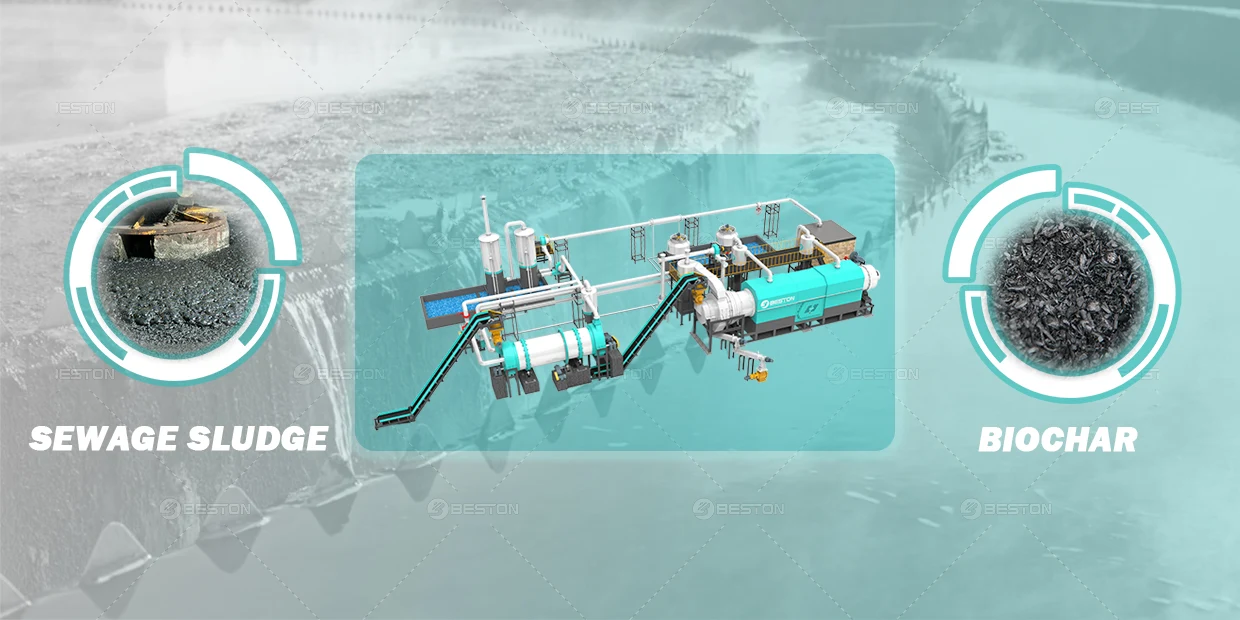
Policy Drivers Influencing Pyrolysis Plant Adoption Worldwide
The global push toward sustainable waste management and circular economy principles has catalyzed interest in advanced thermal conversion technologies. Among these, pyrolysis has emerged as a prominent solution, enabling the transformation of plastic, tire, and other organic wastes into valuable fuels and byproducts. Adoption rates of pyrolysis plants are increasingly shaped by regulatory frameworks, economic incentives, and environmental mandates, creating distinct market dynamics in different regions.
Environmental Regulations and Emission Standards
Strict environmental regulations have become a central driver for pyrolysis plant deployment. Countries with stringent emission controls incentivize industries to adopt cleaner waste-to-energy solutions. For instance, governments in Europe have introduced limits on landfill usage and mandated reductions in plastic and tire disposal, thereby indirectly encouraging facilities like a Pyrolysis Plant in Romania. Compliance with air quality standards often necessitates the integration of advanced gas scrubbing and catalytic systems, features that top pyrolysis equipment manufacturers now routinely incorporate. These regulatory pressures ensure that only technologically robust and environmentally compliant systems are economically viable.

Financial Incentives and Subsidies
Economic instruments are equally influential. Tax credits, feed-in tariffs, and grants for renewable energy projects lower the capital barrier for investors. In Southeast Asia, financial incentives have accelerated the deployment of pyrolysis plants in emerging markets, such as a pyrolysis plant in Indonesia. Here, government-backed subsidies cover part of the equipment costs or operational expenses, making waste-to-fuel conversion projects more attractive. Additionally, some jurisdictions offer preferential loan rates for projects that demonstrate a measurable reduction in carbon footprint, further strengthening the business case for adopting pyrolysis technology.

Circular Economy and Resource Recovery Policies
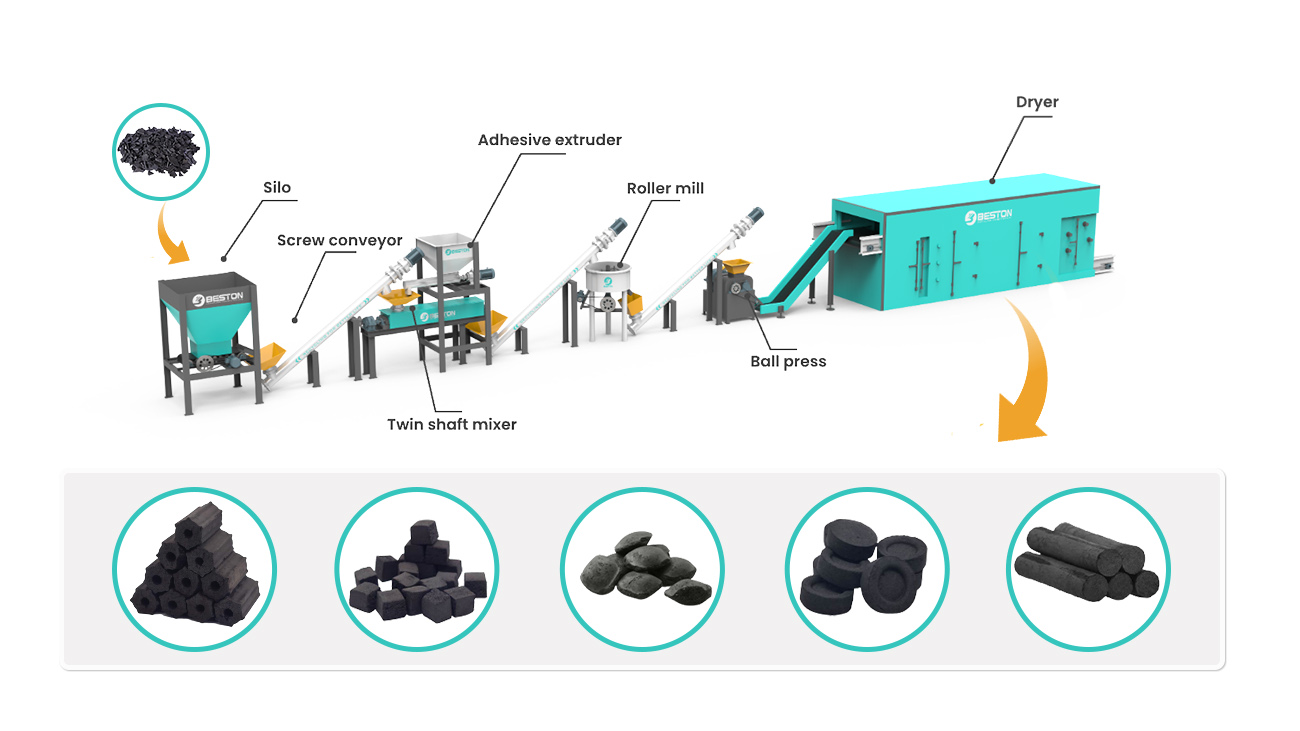
Policies promoting resource recovery and circular economy principles also drive pyrolysis adoption. Legislations that encourage the reutilization of plastic waste, tire residues, and industrial sludge create a demand for facilities capable of converting these materials into reusable products. In countries like Turkey, the introduction of extended producer responsibility (EPR) frameworks has facilitated the establishment of pyrolysis plants, ensuring that producers take responsibility for end-of-life waste. Pyrolysis plants not only address waste diversion targets but also provide a renewable feedstock stream, aligning industrial operations with national sustainability goals.
International Standards and Cross-Border Collaboration
Global standards and cross-border environmental agreements influence the operational parameters and adoption rate of pyrolysis technology. Compliance with international norms on emissions, energy efficiency, and safety protocols is often mandatory for export-oriented projects. Pyrolysis plant in Romania systems that meet these universal criteria, enabling plants in diverse markets—from Europe to Asia—to function efficiently while remaining internationally accredited. As environmental diplomacy strengthens, countries are increasingly looking at pyrolysis as a strategic tool to fulfill both domestic waste management objectives and global climate commitments.
Public Awareness and Policy Advocacy
Public awareness campaigns and advocacy by environmental NGOs further accelerate adoption. Policymakers are under pressure to implement legislation that mitigates visible waste pollution. This socio-political influence complements regulatory frameworks and economic incentives, prompting municipalities and private enterprises to consider projects like a pyrolysis plant in Turkey or Romania. Advocacy for sustainable industrial practices reinforces the narrative that pyrolysis is not merely a technological option but a policy-aligned necessity.
This convergence of regulatory mandates, economic levers, and environmental advocacy has established pyrolysis as a critical technology in modern waste management strategies. Countries worldwide are tailoring policies to accelerate its adoption, resulting in a measurable uptick in projects across emerging and developed markets. Through these policy drivers, pyrolysis plants are positioned as both an industrial asset and a cornerstone of sustainable development.